SAP MM
Mengenal ASAP Metodhology
Just for sharing, biasanya dalam project project SAP, implementor akan menggunakan project metodhology yang berbasis pada ASAP Roadmap Metodhology. Mengutip dari help.sap.com, saya coba tuliskan kembali dalam blog ini apa sih yang dimaksud ASAP Roadmap metodhology
The implementation of your SAP System covers the following phases:
Project Preparation
In this phase you plan your project and lay the foundations for successful implementation. It is at this stage that you make the strategic decisions crucial to your project. Activities in this phase will consist of Define your project goals and objectives, Clarify the scope of your implementation, Define your project schedule, budget plan, and implementation sequence, Establish the project organization and relevant committees and assign resources
Business Blueprint
In this phase you create a blueprint using the Question & Answer database (Q&Adb), which documents your enterprise’s requirements and establishes how your business processes and organizational structure are to be represented in the SAP System. You also refine the original project goals and objectives and revise the overall project schedule in this phase. In this phase, you configure the requirements contained in the Business Blueprint.
Realization
Baseline configuration (major scope) is followed by final configuration (remaining scope), which can consist of up to four cycles. Other key focal areas of this phase are conducting integration tests and drawing up end user documentation.
Final Preparation
In this phase you complete your preparations, including testing, end user training, system management, and cutover activities. You also need to resolve all open issues in this phase.
Go Live & Support
At this stage you need to ensure that all the prerequisites for your system to go live have been fulfilled. In this phase you move from a pre-production environment to the live system. The most important elements include setting up production support, monitoring system transactions, and optimizing overall system performance.
Cukup jelas kan ya penjelasannya, silakan jika ada comment 🙂
– Radityo Yudhiarto –
Document untuk SAP Goods Movements
Masih terusan posting sebelumnya 🙂
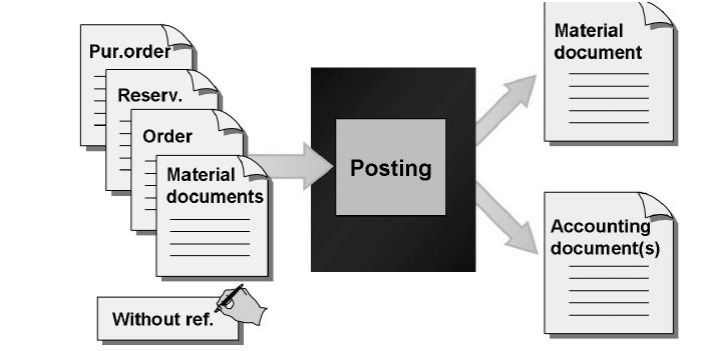
When you enter a goods movement, you can work with or without a reference document. You can enter a goods receipt, for example, with reference to a production order or to a purchase order. However, you can also enter all the necessary data manually. Documents that are created for posting goods movements and are the basis for the quantity and value update also serve as verification for the movement. The bookkeeping principle no posting without document is valid here.
Material document
The material document serves as verification for the goods movement and as a source of information for all subsequent applications. The material document consists of a header and at least one item. The header contains general data about the movement type, such as the date and delivery note number. The items describe the individual movements.A material document is identified by the document number and the material document year.
Accounting document
If the movement is relevant for Financial Accounting (in other words, if the movement leads to an update of the G/L accounts) the system creates an accounting document parallel to the material document.
In some cases — for example, for two material document items with different plants that belong to different company codes — the system creates several accounting documents for one material document. The G/L accounts affected by a goods movement are updated by automatic account determination.An accounting document is identified by the company code, the document number, and the fiscal year
Semoga membantu,
– Radityo Yudhiarto –
Definisi SAP Goods Movement
Co Pas dari MM training module, refresh dulu dari teknikal 🙂
Goods movements include both externaland internal movements. In general, a transaction that causes a stock change is marked as a goods movement. You can distinguish between goods receipts, goods issues, stock transfers, and transfer postings.
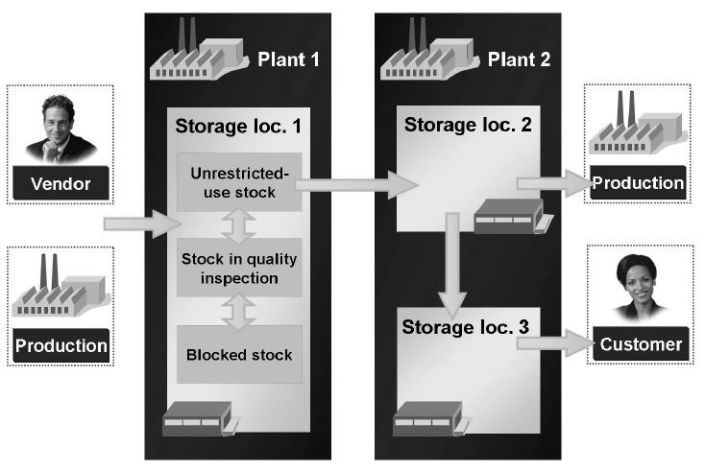
A goods receipt (GR) is a goods movement in which the receipt of goods from both an external vendor and from production is posted. A goods receipt leads to an increase of warehouse stock.
A goods issue (GI) is a goods movement in which a material withdrawal, goods issue, material consumption, or goods shipment is posted to a customer. A goods issue leads to a decrease of warehouse stock.
A stock transfer is removal of materials from a particular storage location and placement into another storage location. Stock transfers can take place both within the same plant and between two plants.
A transfer posting is a superordinate term for stock transfers and changes the stock identification or qualification of a material, regardless of whether the posting is linked to a physical movement or not. Examples of a transfer posting include the release of the stock for quality inspection, the transfer posting from material to material, or the transfer of consignment material.
Semoga bermanfaat,
– Radityo Yudhiarto –